A business plan is a written document that describes your business’s goals and objectives and details how you intend to achieve these goals.
The main purpose of a business plan is to provide investors, lenders and other stakeholders with the information they need to make decisions about your company. It’s also an opportunity for you to think through your strategy and set clear goals for your business.
A good business plan should:
Describe the industry in which you operate and what sets your company apart from others in the field. This can include information on market size, industry trends and competitors.
Outline your target market — who will buy your products or services? What features do they want in their products? How much money do they have to spend?
Outline the financial projections for your business over time, including revenue projections, operating expenses, capital expenditures and cash flow projections.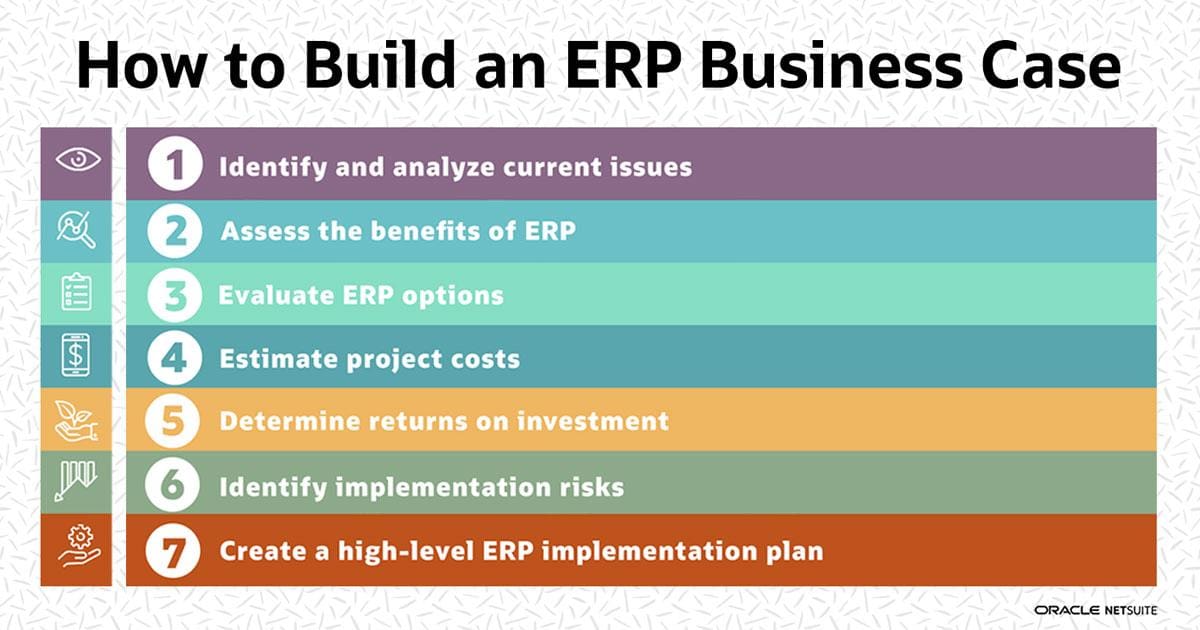
Business plan for erp implementation
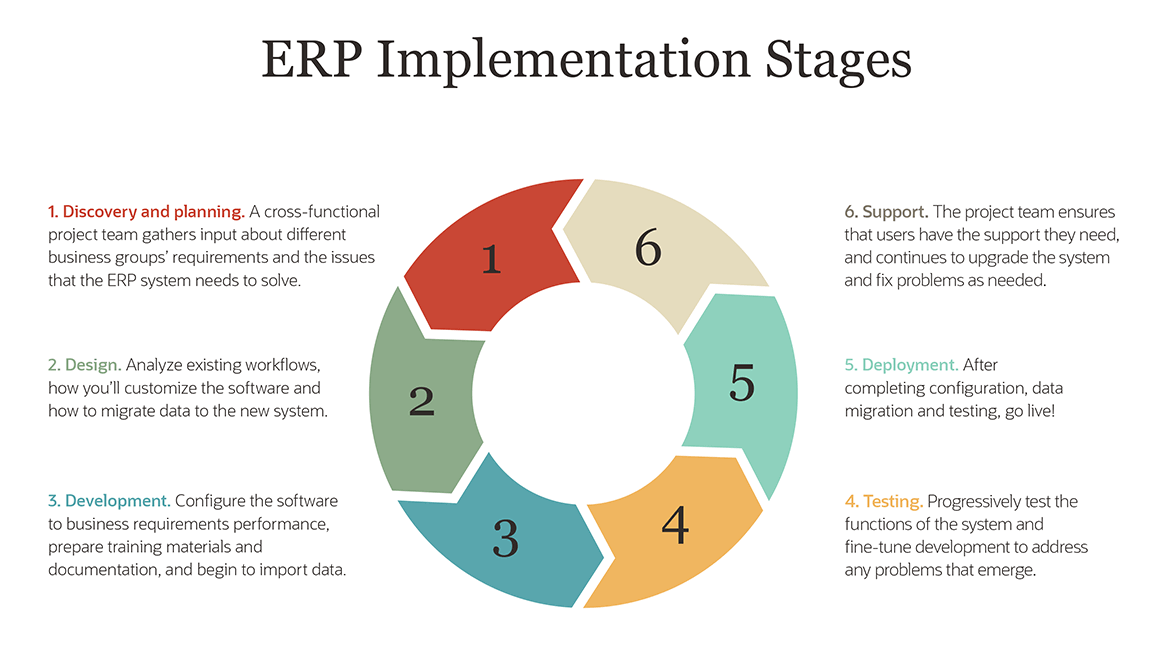
The implementation of an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system is a major undertaking, with potentially far reaching consequences for the business. Although many organisations are now implementing ERP systems, there is still much debate about what constitutes a successful implementation.
In this article we look at some of the issues surrounding successful ERP implementations and provide some advice on how to improve your chances of success.
Successful ERP Implementation: The Key Factors
There are a number of factors that contribute to the success or failure of an ERP implementation project:
1. The business case must be sound and supportable. This may seem obvious but it’s surprising how often companies embark on projects without fully understanding why they’re doing it in the first place. A good business case will clearly explain why implementing an ERP system is necessary and which specific benefits it will deliver for the business. It should also include a detailed explanation of how each benefit will be calculated and measured (see below).
2. Senior management support is vital for any project involving significant investment or change – especially one as large as an ERP implementation! Without senior management support it’s unlikely that any project will succeed; however good its foundations may appear at first glance. Without this level
ERP business cases are used to justify the investment in enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This document is used by organizations to convince their stakeholders that an ERP system will help them achieve their strategic objectives.
ERP Business Case Examples:
A successful ERP Business Case example should include the following sections:
Executive Summary: A brief summary of your entire plan, which includes a description of your company, the problem that you are trying to solve and how this solution will help you solve it.
Business Objectives: The objectives of your project. This section should include your overall goal and specific objectives for each phase of the project.
Market Analysis: An analysis of your market position, trends and competitors. This section should include information about industry growth rates, potential barriers to entry, market size and competitor activities within your industry sector. It should also include information on market trends such as new product launches or changes in customer behavior patterns over time.
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis describes your current strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in relation to your competitors within the market place. It provides a snapshot of where you are currently positioned compared to where you want to be positioned in future years if all goes well with this new venture. It’s important that this
The business case for ERP implementation is a detailed document that explains how the company will benefit from the new system. The business case should be written by the project manager and approved by senior management before any software is purchased or installed.
The purpose of a business case is to convince management that an investment in a particular project or process will generate enough profit to pay for itself within a specified time period. The objective is not only to make money, but to make more money than would be made without the investment. In order to do this, you must calculate all costs and benefits associated with the proposed investment and show how they compare with what would happen if no changes were made.
A typical business case includes:
An executive summary that describes your proposal in plain language so that anyone can understand it
Clear, concise descriptions of all key areas of your proposal
A detailed financial analysis to support your recommendation
A list of resources available for further information
The following is an example of a Business Case for ERP Implementation.
ERP Implementation Business Case Sample
The purpose of this business case is to provide justification for the implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system at ABC Company. The company has been using manual systems and processes for its operations since its inception in 1988. However, due to rapid growth, the company is facing several problems with its existing system that include:
Inability to manage large volumes of data in real time.
Inability to share data with suppliers and customers efficiently.
Inability to provide accurate reports on all aspects of the business with any degree of reliability or consistency.
Inability to track inventory levels in real time, causing delays in shipping orders out on time.